We create tremendous amounts of data each day, whether we browse the web, shop online or scroll on social media – our data makes a lot of money for big tech companies like Google, Amazon or Facebook. Today’s data economy is dominated by a few centralized players that keep all the revenue that our data is creating for themselves. We, as the end user of their products, are excluded from earning any monetary value from our data.
Data unions are a paradigm shift that seeks to redistribute wealth and control over data back to the people: made possible by leveraging decentralized technologies for the permissionless transfer of these digital assets. Instead of being the product, members of a data union earn a stake in the organization for providing their data.
What’s a data union?
A data union enables people to earn with their data. A data union is powered by the Data Union framework which is the infrastructure that powers applications to incentivize people for joining a data union and participating in the crowdsourcing of valuable data.
The world’s first data union is Swash, which offers an application as a browser extension that lets users get paid for their data as they browse the web. The browser extension is built utilizing the Data Union framework, which enables Swash to offer a browse-to-earn platform for members – all while retaining the privacy of its users. There are several different applications that you can download and join to earn with your data.
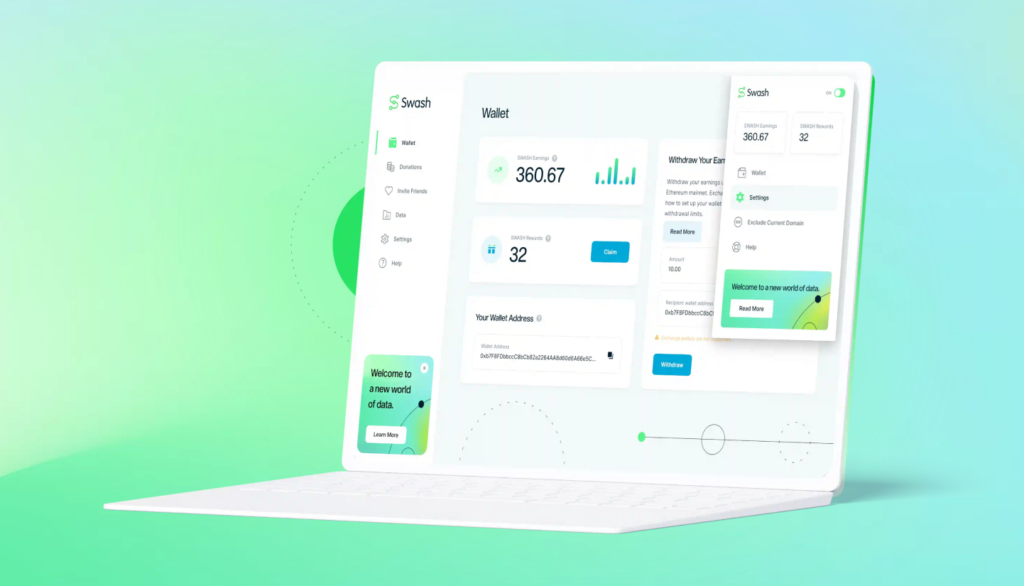
How does it work?
Here is how a typical data union works:
- A data union is an organization with an application where individuals are rewarded for participating in the crowdsourcing of data.
- A user joins as a member of a data union and consents to have their data monetized. Members retain full transparency and control over their data and earn a fair share of money from data sales.
- Members generate data through the application of the data union, which crowdsources data.
- That data is bundled together as a data product and offered on a data marketplace for potential buyers to gain insight.
- The money from data sales is used to reward data union members for providing valuable data.
What data is collected?
The type of data that is collected depends heavily on the organization and its application, or decentralized application (dApp – in the case of web3). In the example of Swash, they collect data about websites that you visit. Which is nothing different from what Google is doing – with the difference being that Swash will actually pay you for your data.
Other data unions focus on different types of data. DIMO, which is another startup utilizing the Data Union framework, crowdsources vehicle data in exchange for their users earning crypto rewards.
How much can I earn?
While an individual’s data alone is close to worth nothing, aggregating user data into a data set from a larger group of people offers attractive insights for other organizations to buy into.
Data economies are projected to generate $13 trillion in new global economic activity by 2030, according to McKinsey. Currently, the amount people can earn with existing data unions is not very high – but that has mainly to do with the fact that the data sets are not as big and not as valuable yet. Data unions are a new concept and have been mainly new grassroots organizations that started their journey and data sets from scratch. As more people join data unions, like Swash, the bigger the data set gets the more value it can be monetized for.
What is the impact data unions can have?
The technology opens up entirely new business opportunities for crowdsourcing data that has never been possible before. The Data Union framework has enabled three startups to raise over $30m in funding. Let’s take a look at one of them and their potential impact: DIMO is a new web3 startup that raised $9m in seed funding last December.
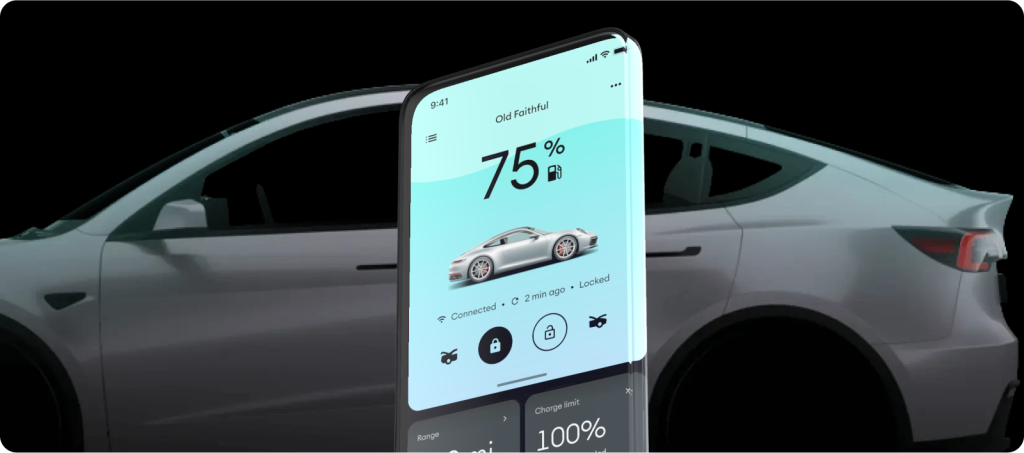
DIMO crowdsources vehicle data from a variety of different vehicles. Diesel and other non smart cars can connect to DIMO via their IoT device. Electric vehicles, smart cars and Tesla drivers can download the DIMO app via their car’s app store. Once the driver connects their car to DIMO, it starts to stream real-time data into the DIMO data union.
data in the automotive world is not very well shared and not very well collected
– Alex Rawitz, co-founder at DIMO
Since in the current automotive world data about cars is stored within silos of each respective car manufacturer, it is going to be very valuable for other organizations in the automotive industry to gain insight about other cars.
Even for governments and nonprofit organizations this data could be valuable for research purposes that lead to more impactful outcomes like improving road safety.
Join or build a data union
Our mission is to disrupt existing data business models by enabling people to sell their data with full transparency, control, and fair revenue sharing.
With the Data Union framework, we can move from the current data monetization industry where the winner takes all to an industry that enables people to earn with their data.
You can now join existing data unions as a member and be rewarded for your data. You can also build a new data union. Are you ready to join forces?